Scope
- The connection of the user's browser to the JOC Cockpit can be secured by HTTPS.
- The connection of the JOC Cockpit - REST Web Service to the JobScheduler Master can be secured by HTTPS.
- This article describes the steps required to set up secure HTTPS communication with Jetty and with the JobScheduler Master.
- Consider the JOC Cockpit - Architecture for an overview of components and connections.
- Consider JobScheduler Universal Agent - HTTPS Agent and Master Authentication for securing the connections between a JobScheduler Master and Agents.
Prerequisites
- The only prerequisite is to have the Java Keytools installed with your Java JRE or JDK.
Certificate Management
Certificate Management for secure connections of user browsers to the JOC Cockpit
Should JOC Cockpit and JobScheduler Master be operated on the same server then no HTTPS connection between both components is required. To secure the JOC Cockpit user interface for HTTPS access by user browsers the following private key and certificates should be in place:
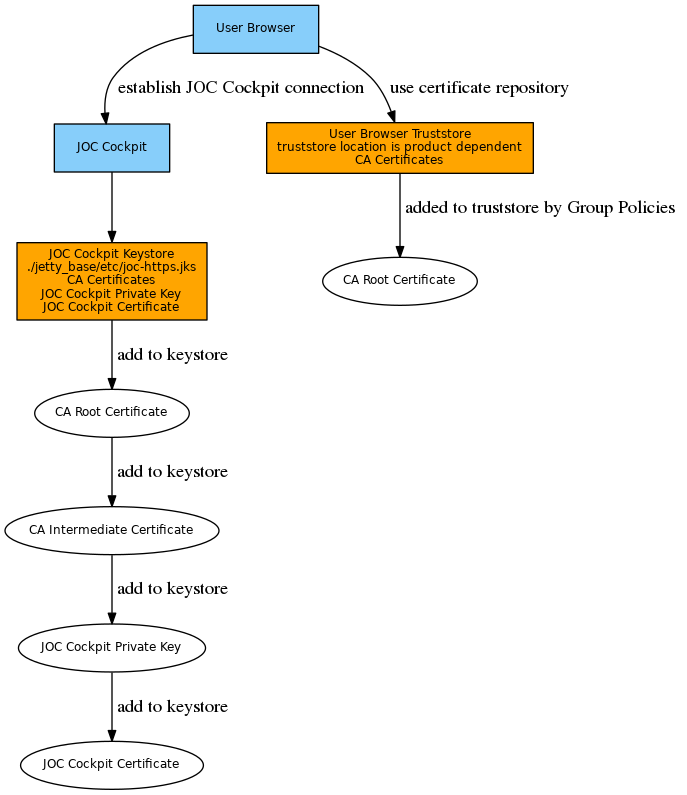
Then proceed with chapter Set up a secure connection of user browsers to the JOC Cockpit
Certificate Management for secure connections of the JOC Cockpit to the JobScheduler Master
Should JOC Cockpit and JobScheduler be operated on different servers then both connections should be secured by HTTPS
- the connection from the user browser to the JOC Cockpit user interface,
- the connection from JOC Cockpit to the Master.
Private keys and public certificates should be distributed as follows:
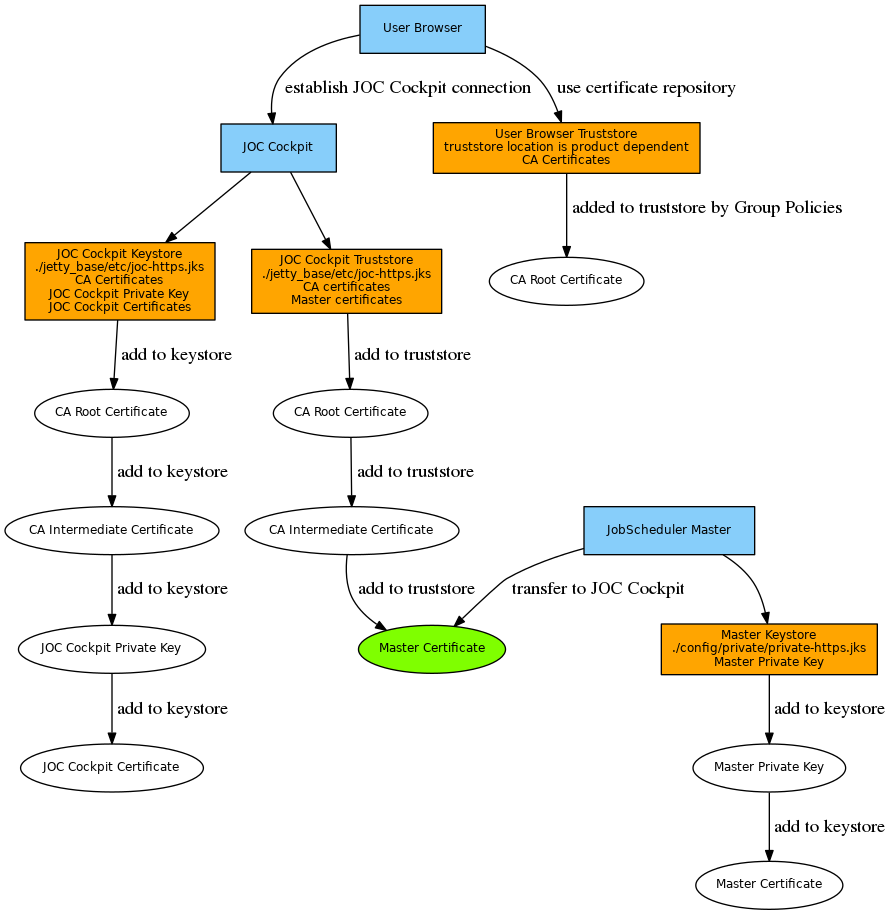
The Master's private key and certificate are added to the Master's keystore. In case of a self-signed certificate the certificate is added to the JOC Cockpit truststore as well. This step can be skipped if a CA-signed certificate is used as the Root Certificate and Intermediate Certificate in the JOC Cockpit truststore are sufficient to verify any Master certificates.
Set up a secure connection of user browsers to the JOC Cockpit
This configuration is applied in order to enable users to access the JOC Cockpit by use of HTTPS with their browser.
In the following the placeholders JOC_HOME, JETTY_HOME and JETTY_BASE are used which locate three directories. If you install Jetty with the JOC installer then
JOC_HOMEis the installation path which is specified during the JOC Cockpit installation:- C:\Program Files\sos-berlin.com\joc (default on Windows)
- /opt/sos-berlin.com/joc (default on Linux)
JETTY_HOME=JOC_HOME/jettyJETTY_BASEis Jetty's base directory which is specified during the JOC Cockpit installation:- C:\ProgramData\sos-berlin.com\joc (default on Windows)
- /home/<setup-user>/sos-berlin.com/joc (default on Linux)
Step 1: Add the HTTPS module to Jetty
On the JOC Cockpit server run the following command and replace the
JETTY_HOMEandJETTY_BASEplaceholders as specified above:Add HTTPS module to Jettyjava -jar "JETTY_HOME/start.jar" -Djetty.home="JETTY_HOME" -Djetty.base="JETTY_BASE" --add-to-start=https
- Having executed the above command you should find a new folder
JETTY_BASE/etc- Jetty expects a Keystore in this folder with the name "keystore" by default.
You can copy the
JETTY_HOME/etc/keystorefile toJETTY_BASE/etc/keystoreas a workaround, however, you should use your own Keystore for later on (see step 2). It is not recommended to use the default Keystore as in particular, the Keystore fromJETTY_HOME/etc/keystoreexpires after a short lifetime.Jetty doesn't start if it doesn't find a keystore corresponding its settings.
- In addition some entries in the
JETTY_BASE/start.iniconfiguration file for SSL settings such as the HTTPS port are added.
Step 2: Create the Java Keystore for Jetty
- On the JOC Cockpit server create the Java Keystore using the Keytools from your Java JRE or JDK.
- Generate the Java Keystore in JKS or PKCS12 format with the private key and public certificate for Jetty. The below examples suggest one possible approach for certificate management, however, there may be other ways how to achieve similar results.
Example for use of self-signed certificate with JKS keystore format
Example how to generate a JKS Keystore with private key and public certificate# generate JOC Cockpit private key with alias name "joc-https" in a keystore (joc-https.jks) # use the fully qualified hostname (FQDN) and name of your organization for the distinguished name keytool -genkey -alias "joc-https" -dname "CN=hostname,O=organization" -validity 1461 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keypass jobscheduler -keystore "JETTY_BASE/etc/joc-https.jks" -storepass jobscheduler
Example for use of self-signed certificate with PKCS12 keystore format
Example how to generate a PKCS12 Keystore with private key and public certificate# generate JOC Cockpit private key with alias name "joc-https" in a keystore (joc-https.p12) # use the fully qualified hostname (FQDN) and name of your organization for the distinguished name # consider that PKCS12 keystores require to use the same key password and store password keytool -genkey -alias "joc-https" -dname "CN=hostname,O=organization" -validity 1461 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keypass jobscheduler -keystore "JETTY_BASE/etc/joc-https.p12" -storepass jobscheduler -storetype PKCS12
Example for use of CA signed certificate with PKCS12 keystore format:
Example how to add a CA signed private key and public certificate to a PKCS12 Keystore# should your JOC Cockpit private key and certificate by provided with a .jks keystore (keypair.jks) then temporarily convert the keystore to pkcs12 (keystore.p12) # for later use with openssl, assuming the alias name of the JOC Cockpit private key is "joc-https" # keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keypair.jks -destkeystore keystore.p12 -deststoretype PKCS12 -srcalias joc-https # assuming your JOC Cockpit private key from a pkcs12 keystore (keystore.p12), store the JOC Cockpit private key to a .key file in PEM format (joc-https.key) openssl pkcs12 -in keystore.p12 -nocerts -out joc-https.key # concatenate CA root certificate and CA intermediate certificates to a single CA Bundle certificate file (ca-bundle.crt) cat RootCACertificate.crt > ca-bundle.crt cat CACertificate.crt >> ca-bundle.crt # Export JOC Cockpit private key (joc-https.key), JOC Cockpit public certificate in PEM format (joc-https.crt) and CA Bundle in PEM format (ca-bundle.crt) to a new keystore (joc-https.p12) # assume the fully qualified hostname (FQDN) of the JOC Cockpit server to be "joc.example.com" openssl pkcs12 -export -in joc-https.crt -inkey joc-https.key -chain -CAfile ca-bundle.crt -name joc.example.com -out joc-https.p12 # should you require use of a .jks keystore type then convert the pkcs12 keystore assuming the alias name of the JOC Cockpit private key to be "joc-https" # keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore joc-https.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -destkeystore joc-https.jks -deststoretype JKS -srcalias joc-https
Explanations
- Replace the
JETTY_BASEplaceholder as specified above. - The
-dnameoption specifies the certificate issuer, therefore use your own set of CN, OU, DC that specify the issuer's distinguished name. The O setting is required for the issuer. - The
-keypassoption accepts the password that you will need later on to manage your private key. - The
-keystoreoption specifies the location of your Keystore file. - The
-storepassoption specifies the password for access to your Keystore file. - The
-storepassoption is used for the PKCS12 keystore format, this option is not required for the JKS keystore format.
- Replace the
- Generate the Java Keystore in JKS or PKCS12 format with the private key and public certificate for Jetty. The below examples suggest one possible approach for certificate management, however, there may be other ways how to achieve similar results.
- Alternatively apply a private key and certificate that are issued by your organization or a trusted authority.
Step 3: Configure Jetty
Edit the following entries in the
JETTY_BASE/start.iniconfiguration file corresponding to the Java Keystore:## Keystore file path (relative to $jetty.base) jetty.sslContext.keyStorePath=etc/joc-https.jks ## Truststore file path (relative to $jetty.base) jetty.sslContext.trustStorePath=etc/joc-https.jks ## Keystore password jetty.sslContext.keyStorePassword=jobscheduler ## KeyManager password (same as keystore password for pkcs12 keystore type) jetty.sslContext.keyManagerPassword=jobscheduler ## Truststore password jetty.sslContext.trustStorePassword=jobscheduler
Explanations- Specify the location of the Keystore with the
keyStorePathsetting and optionally of the Truststore with thetrustStorePathsetting. A location relative to theJETTY_BASEdirectory can be specified. - Specify the password for your Keystore with the
keyStorePasswordsetting. If a Truststore is used then specify its password accordingly with thetrustStorePasswordsetting. - The password specified with the
keyManagerPasswordsetting is used for access to your private key. The same password as for thekeyStorePasswordsetting has to be used for a PKCS12 keystore type.
- Specify the location of the Keystore with the
Specify the HTTPS port with the following entry of the
JETTY_BASE/start.iniconfiguration file (default HTTPS port is 48446):## Connector port to listen on jetty.ssl.port=48446
Step 4: Deactivate HTTP Access
To deactivate HTTP access simply add a comment to the following module directive in your JETTY_BASE/start.ini configuration file like this:
# Module: http # --module=http
Set up a secure connection from the JOC Cockpit to the JobScheduler Master
This configuration is applied in order to secure the connection if JOC Cockpit and JobScheduler Master are not operated on the same server. If not otherwise stated then the steps for HTTPS configuration are performed on the server that hosts the JobScheduler Master.
Step 1: Create the Java Keystore
- On the JobScheduler Master server create the Java Keystore using the Keytools from your Java JRE or JDK. The below examples suggest one possible approach for certificate management, however, there may be other ways how to achieve similar results.
- Generate the Java Keystore with the private key and the public certificate for the JobScheduler Master and export the certificate to a second Keystore that is later on used by the JOC Cockpit.
Example for use of self-signed certificate with JKS keystore format
Example how to generate a JKS Keystore with private key and public certificate# generate Master private key with alias name "master-https" in a keystore (private-https.jks) # use the fully qualified hostname (FQDN) and name of your organization for the distinguished name keytool -genkey -alias "master-https" -dname "CN=hostname,O=organization" -validity 1461 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keypass jobscheduler -keystore "SCHEDULER_DATA/config/private/private-https.jks" -storepass jobscheduler
Example for use of self-signed certificate with PKCS12 keystore format
Example how to generate a PKCS12 Keystore with private key and public certificate# generate Master private key with alias name "master-https" in a keystore (private-https.p12) # use the fully qualified hostname (FQDN) and name of your organization for the distinguished name # consider that PKCS12 keystores require to use the same key password and store password keytool -genkey -alias "master-https" -dname "CN=hostname,O=organization" -validity 1461 -keyalg RSA -keysize 2048 -keypass jobscheduler -keystore "SCHEDULER_DATA/config/private/private-https.pk12" -storepass jobscheduler -storetype PKCS12
- Example for use of CA signed certificate with PKCS12 keystore formatExample how to add a CA signed private key and public certificate to a PKCS12 Keystore
# should your Master private key and certificate by provided with a .jks keystore (keypair.jks) then temporarily convert the keystore to pkcs12 (keystore.p12) # for later use with openssl, assuming the alias name of the Master private key is "master-https" # keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore keypair.jks -destkeystore keystore.p12 -deststoretype PKCS12 -srcalias master-https # assuming your Master private key from a pkcs12 keystore (keystore.p12), store the Master private key to a .key file in PEM format (master-https.key) openssl pkcs12 -in keystore.p12 -nocerts -out master-https.key # concatenate CA root certificate and CA intermediate certificates to a single CA Bundle certificate file (ca-bundle.crt) cat RootCACertificate.crt > ca-bundle.crt cat CACertificate.crt >> ca-bundle.crt # Export Master private key (master-https.key), Master public certificate in PEM format (master-https.crt) and CA Bundle in PEM format (ca-bundle.crt) to a new keystore (private-https.p12) # assume the fully qualified hostname (FQDN) of the Master server to be "master.example.com" openssl pkcs12 -export -in master-https.crt -inkey master-https.key -chain -CAfile ca-bundle.crt -name master.example.com -out private-https.p12 # should you require use of a .jks keystore type then convert the pkcs12 keystore assuming the alias name of the Master private key to be "master-https" # keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore private-https.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -destkeystore private-https.jks -deststoretype JKS -srcalias master-https
Explanations
- Replace the
SCHEDULER_DATAplaceholder as specified above. - The
-dnameoption specifies the certificate issuer, therefore use your own set of CN, O, OU, DC that specify the issuer's distinguished name. The O setting is required for the issuer. - The
-keypassoption accepts the password that you will need later on to manage your private key. With the default password being used no further settings are required as explained below. - The
-keystoreoption specifies the location of your Keystore file.- The Keystore file should be in reach of the JobScheduler Master, it is therefore recommended to use a sub-folder
privatein the./configdirectory. - Using the default file name
"private-https.jks"will save the effort of adding further settings as explained above.
- The Keystore file should be in reach of the JobScheduler Master, it is therefore recommended to use a sub-folder
- The
-storepassoption specifies the password for access to your Keystore file. For the handling of the default password the same applies as stated with the-keypassoption. - The
-storetypeoption is used for the PKCS12 keystore format, this option is not required for the JKS keystore format.
- Replace the
- If not otherwise configured then the JobScheduler Master by default uses the password
jobschedulerfor the respective Keystore. - If you choose an individual password for the JobScheduler Master Keystore then adjust the following properties in the
SCHEDULER_DATA/config/private/private.confconfiguration file:- Explanations
jobscheduler.master.webserver.https.keystore.fileis used for the path to the Keystorejobscheduler.is used for the Keystore passwordmaster.webserver.https.keystore.passwordjobscheduler.is used for the password of your private keymaster.webserver.https.keystore.key-password
Example
Example for private.conf file specifying the Master Keystorejobscheduler.master.webserver.https.keystore { file = "C:/ProgramData/sos-berlin.com/jobscheduler/master110/config/private/private-https.jks" # Backslashes are written twice (as in JSON notation): # file = "\\\\other-computer\\share\\my-keystore.jks" password = "jobscheduler" key-password = "jobscheduler" }
- Explanations
- Generate the Java Keystore with the private key and the public certificate for the JobScheduler Master and export the certificate to a second Keystore that is later on used by the JOC Cockpit.
- Export the JobScheduler Master public certificate for use with the JOC Cockpit Web Service
Example for export with JKS keystore format
Example how to export the Master public certificate from a JKS Keystore# export Master public certificate from keystore (private-https.jks) identified by its alias name (master-https) to a file in PEM format (master-https.crt) keytool -exportcert -rfc -noprompt -file "master-https.crt" -alias "master-https" -keystore "SCHEDULER_DATA/config/private/private-https.jks" -storepass jobscheduler
Example for export with PKCS12 keystore format
Example how to export the Master public certificate from a PKCS12 Keystore# export Master public certificate from keystore (private-https.p12) identified by its alias name (master-https) to a file in PEM format (master-https.crt) keytool -exportcert -rfc -noprompt -file "master-https.crt" -alias "master-https" -keystore "SCHEDULER_DATA/config/private/private-https.p12" -storepass jobscheduler -storetype PKCS12
- The exported public certificate of each JobScheduler Master has to be imported to the Java Truststore that is used by the JOC Cockpit.
Step 2: Set up Authentication to JobScheduler Master
- The JobScheduler Master HTTPS web service is only accessible to authenticated users that are identified by the JobScheduler ID.
- The JobScheduler ID is specified on installation of a JobScheduler Master and is a unique string.
- Should you operate a JobScheduler cluster then the same JobScheduler ID is used that has been assigned to all Masters during setup. Do not mix up the JobScheduler ID and the suffix
-backupthat is applied to a Backup Master installation directory.
- The JobScheduler Master expects HTTP Basic Authentication.
The credentials are used from
SCHEDULER_DATA/config/private/private.confconfiguration file that offers an entry like this:jobscheduler.master.auth.users { JOBSCHEDULER_ID = "HASH_SCHEME:HASHED_PASSWORD" }The
HASH_SCHEMEis specified by the prefix "plain" and is followed by the password:jobscheduler.master.auth.users { jobscheduler_prod = "plain:secret" }
Step 3: Set up the JobScheduler Master for HTTPS
Specify the ports with the <
config>element in theSCHEDULER_DATA/config/scheduler.xml configurationfile like this:- the HTTP port is required but is limited to the localhost network interface with the
http_portattribute the HTTPS port with the
https_portattribute of like this:<spooler> <config http_port="localhost:40444" https_port="48444" mail_xslt_stylesheet="config/scheduler_mail.xsl"> <!-- other elements --> </config> </spooler>
- the HTTP port is required but is limited to the localhost network interface with the
Step 4: Configure the JOC Cockpit Web Service Truststore
On the JOC Cockpit server perform the following steps:
- The JOC Cockpit Keystore can also be used as a Truststore where the certificates of a number of JobScheduler Masters are imported.
Example for JKS Keystore
Example how to import the Master public certificate to JOC Cockpit JKS Keystore# import Master public certificate from a file in PEM format (master-https.crt) identified by its alias name (master-https) to the JOC Cockpit JKS keystore (joc-https.jks) keytool -importcert -noprompt -file "master-https.crt" -alias "master-https" -keystore "JETTY_BASE/etc/joc-https.jks" -storepass jobscheduler -trustcacerts
Example for PKCS12 Keystore
Example how to import the Master public certificate to JOC Cockpit PKCS12 Keystore# import Master public certificate from a file in PEM format (master-https.crt) identified by its alias name (master-https) to the JOC Cockpit PKCS12 keystore (joc-https.p12) keytool -importcert -noprompt -file "master-https.crt" -alias "master-https" -keystore "JETTY_BASE/etc/joc-https.p12" -storepass jobscheduler -storetype PKCS12 -trustcacerts
Explanations
- The alias of each certificate has to be unique for the target Keystore.
- Alternatively, you can import the JobScheduler Master certificates into the default Java Truststore (
JAVA_HOME/lib/security/cacerts) of the Java installation which is used by Jetty, however, this setting will be lost if you switch the Java version.
If you use the Keystore of your JOC Cockpit Web Service in Jetty as the Truststore of the JobScheduler Master certificates then add the location of the Truststore to the
JETTY_BASE/resources/joc/joc.propertiesconfiguration file like this:Example for JKS keystore format
### Location of the Java truststore that contains the certificates of each ### JobScheduler Master for HTTPS connections. The path can be absolute or relative ### to joc.properties truststore_path = ../../etc/joc-https.jks truststore_password = jobscheduler
Example for PKCS12 keystore format
### Location of the Java truststore that contains the certificates of each ### JobScheduler Master for HTTPS connections. The path can be absolute or relative ### to joc.properties truststore_path = ../../etc/joc-https.p12 truststore_type = PKCS12 truststore_password = jobscheduler
- Explanations
- The relative path from the above example looks up the Keystore in the
JETTY_BASE/etcdirectory.
- The relative path from the above example looks up the Keystore in the
The hostname verification can be added optionally in the
JETTY_BASE/resources/joc/joc.propertiesconfiguration file.################################################################################ ### Should hostname verification be carried out for https certificate. ### Default false https_with_hostname_verification = true
Caveat
- In order to apply modifications to ./config/private/private.conf files of the Master or to any configuration files of JOC Cocckpit a restart of the respective component is required.